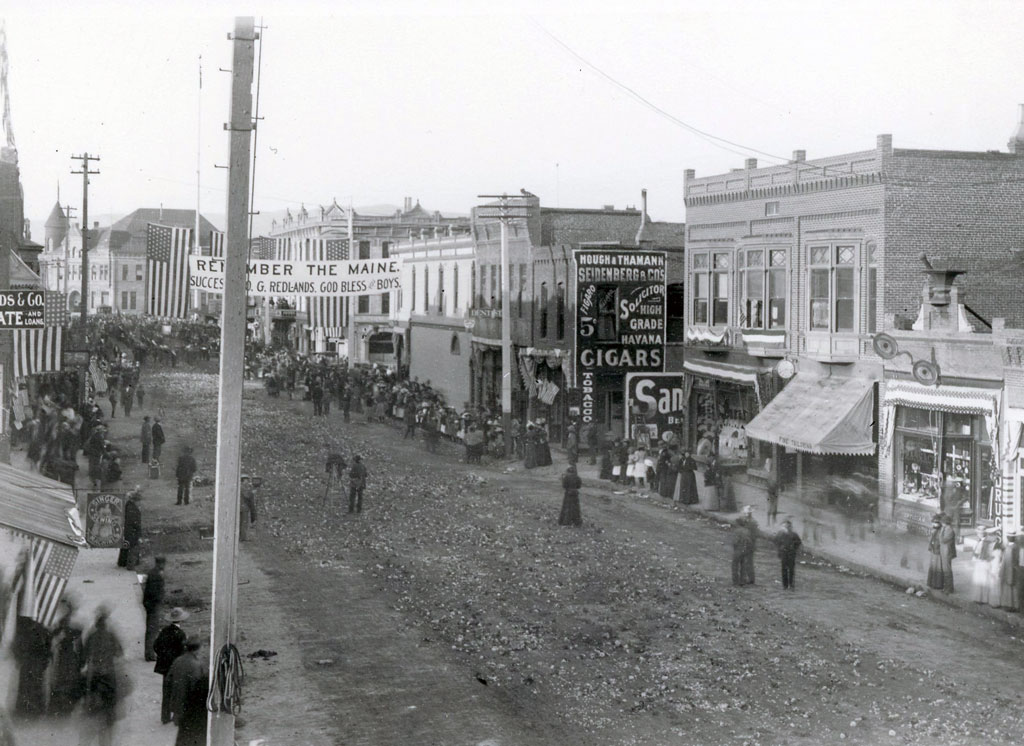
Facts and History about San Bernardino County
San Bernardino County 1800-1850
Act to Create San Bernardino County
April 26, 1853, San Bernardino County created from parts of Los Angeles and San Diego Counties.

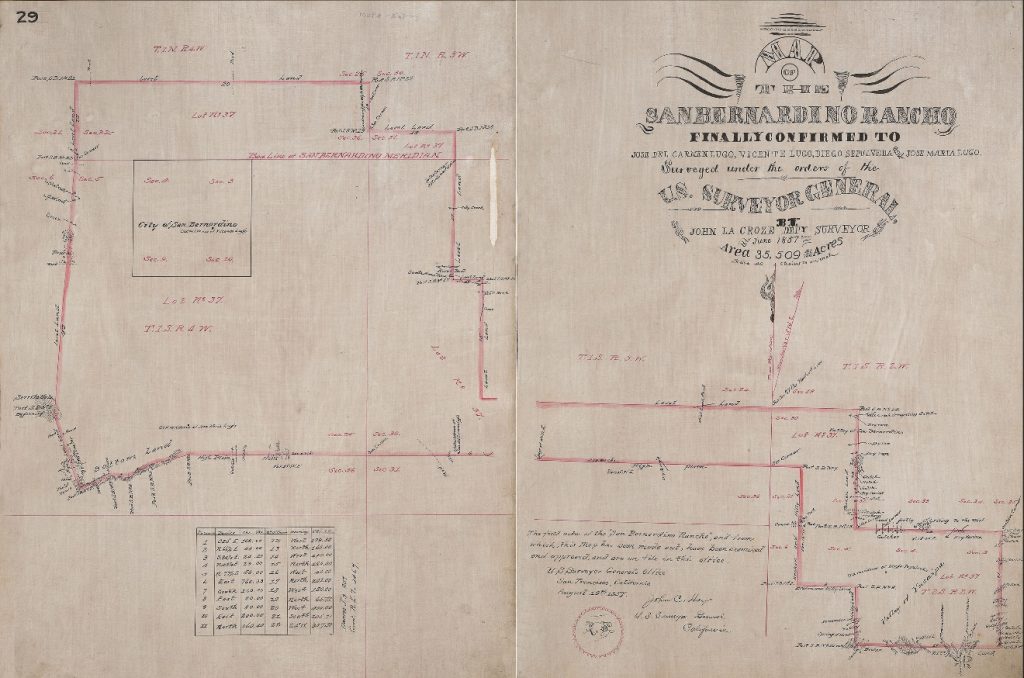
San Bernardino Rancho Map
1842, the Rancho San Bernardino, 37, 700 acres, was granted to José del Carmen Lugo, José Maria Lugo, Vincente Lugo, and Jose Diego Sepulveda.
1851, Lugo’s sold the Rancho to members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints who started a settlement in what would now be downtown San Bernardino.
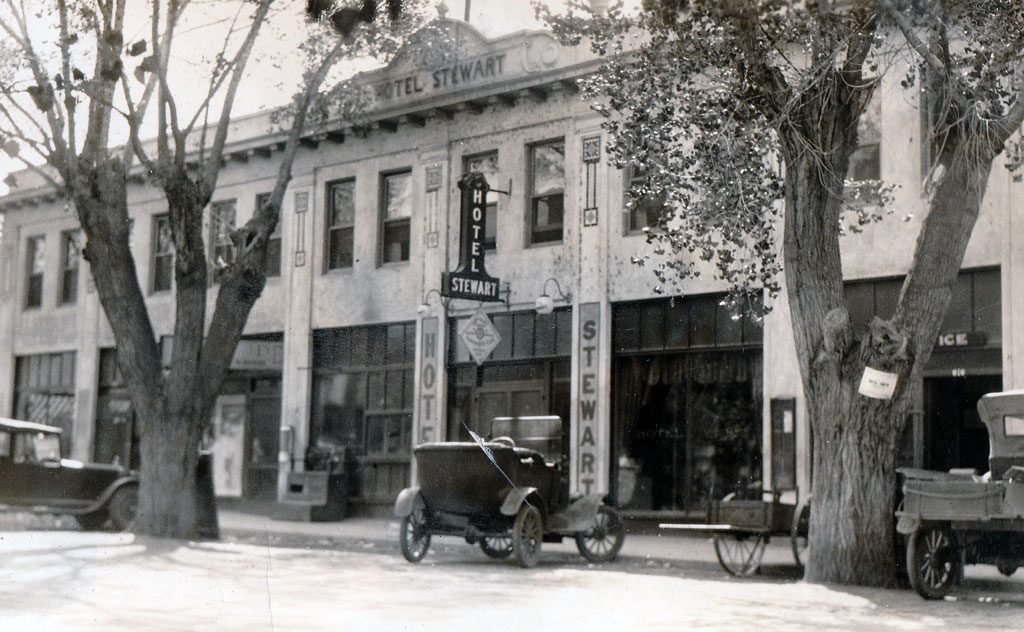
1854, San Bernardino City incorporated and named county seat.
San Bernardino received its name from the first missionaries that founded the Mission San Gabriel outpost at the Asistencia; they called it after Bernardino of Siena because of the snowcapped mountains which reminded the monks of Siena, Italy.
San Bernardino County 1850-1900
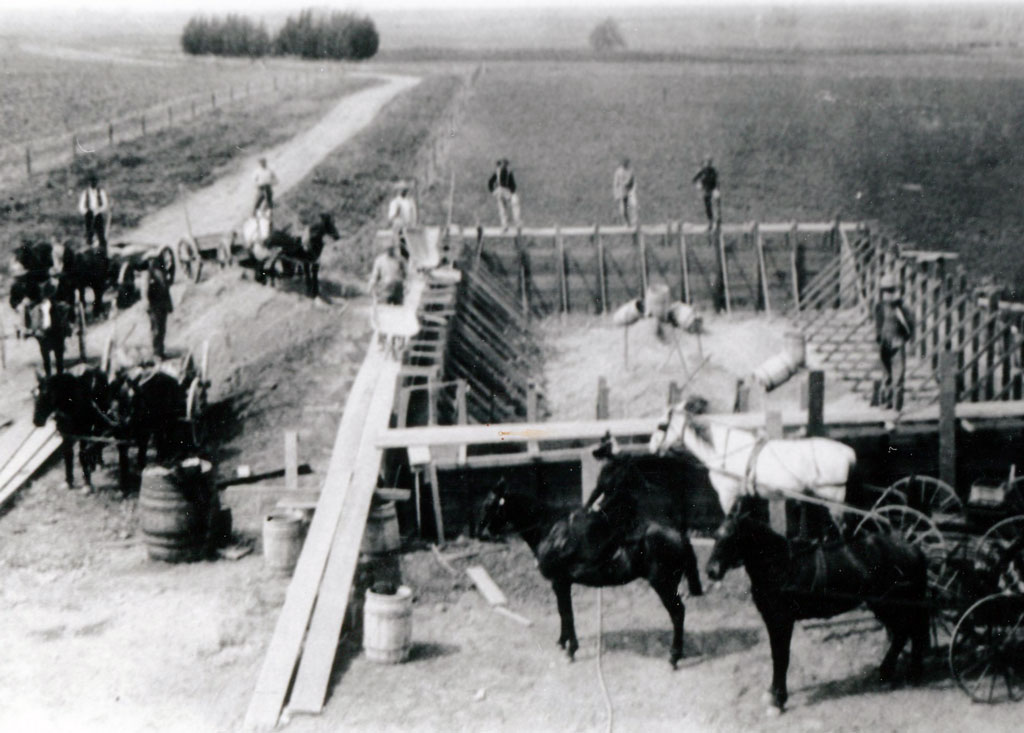
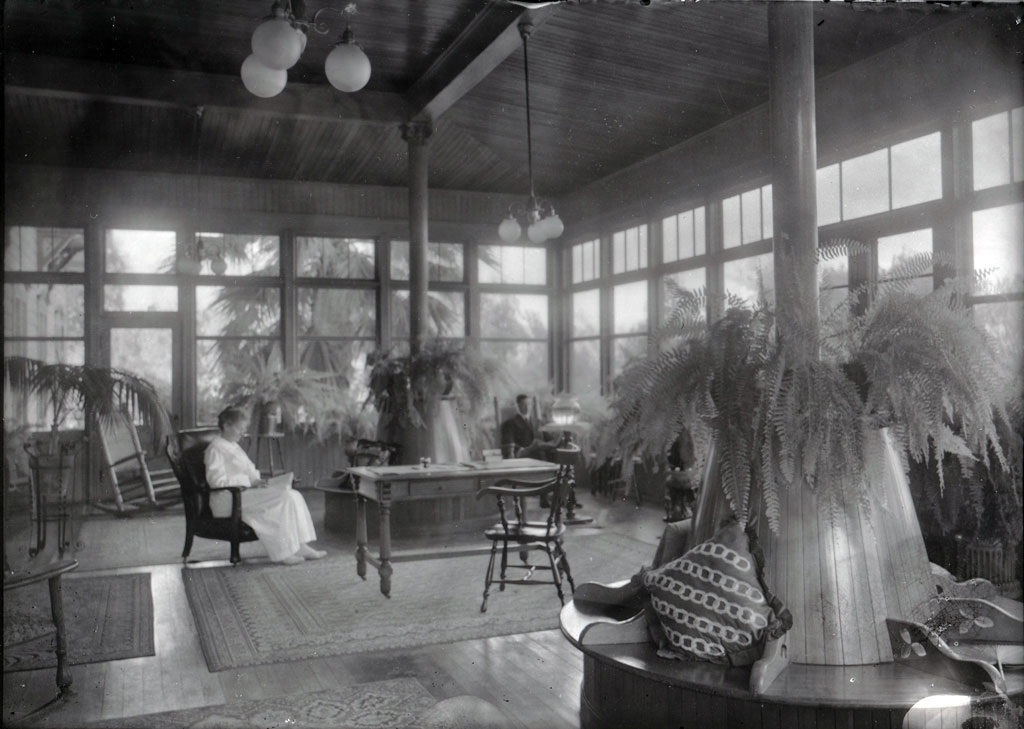
Rains House
1858, María Merced Williams and John Rains built a brick house.
1858, Maria Merced Tapia de Prudhomme and Leon Victor Prudhomme sold the Rancho Cucamonga to the Rains. The Prudhomme’s had received the Rancho Cucamonga from her father Tiburcio Tapia who was granted the land in 1839.
Prudhomme is credited with planting the first grapevines and starting a vineyard in the 1840s.
The Rains added to the existing vineyard of over 160 acres.
1971, Casa de Rancho Cucamonga Historical Society, a group of community members who had saved the structure from destruction sold to structure to the County as part of the San Bernardino County Museum.
2022, the San Bernardino County Board of Supervisors voted to change the site name to María Merced Williams and John Rains House.


Holcomb Valley
1860, William Holcomb and Ben Ware discover gold in Holcomb Valley. Holcomb Valley was the largest gold discovery in Southern California. A town named Belleville was created in the area.
There is a myth that Belleville was almost the County seat. The story is that ballots for the switch in county seat were being counted around an open bonfire when one of the ballot boxes from Belleville was kicked into the fire and destroyed. When the count was completed, Belleville had lost the county seat election by two votes.
The California Constitution allows for a change in county seat only through legislative action, or through the authority of the voters of the county. There was no legislative action on record in State Records. Items up for election are required to be listed in the Board of Supervisor minutes and to be posted in the newspaper, there is no listing for the change of the County seat in either.
William Holcomb was the first elected Justice of the Peace for Belleville, he later went on to serve as a San Bernardino County Assessor.

Trona
1862, John W. Searles discovered borax on the dry barren surface of Searles Lake while prospecting for gold and silver with three other people in the Slate mountain range, but his discovery went unrecognized.
1872, after seeing Francis (Borax) Smith’s operation of Borax recovery in Nevada Searles realized what he had discovered.
1873, John W. Searles staked a claim to 640 acres of lake and formed The San Bernardino Borax Mining Company.
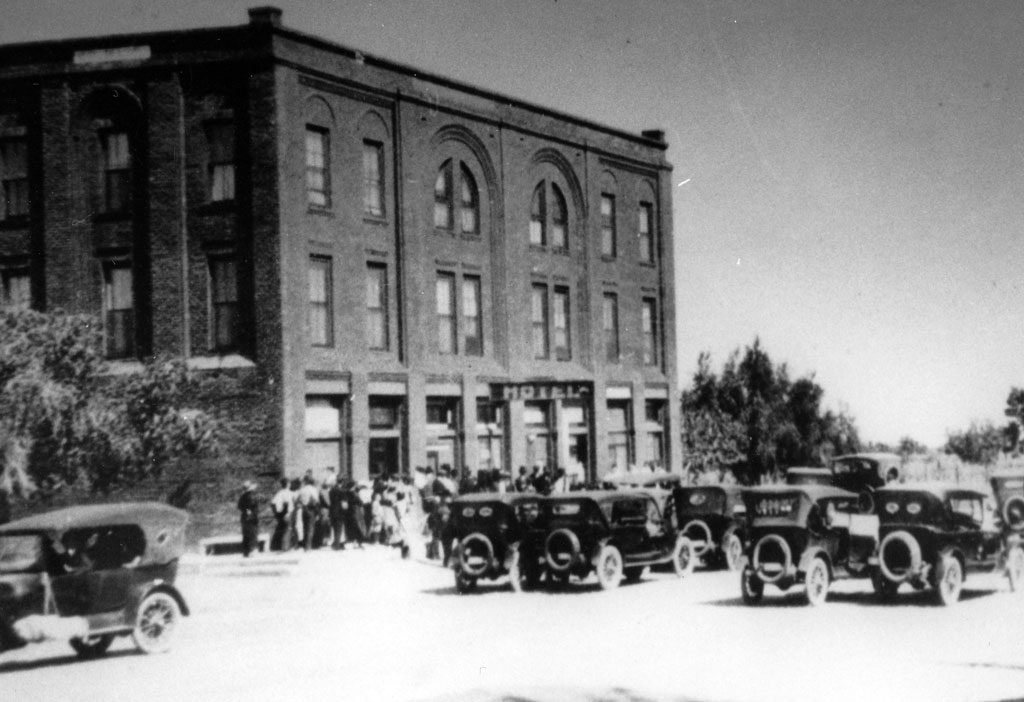
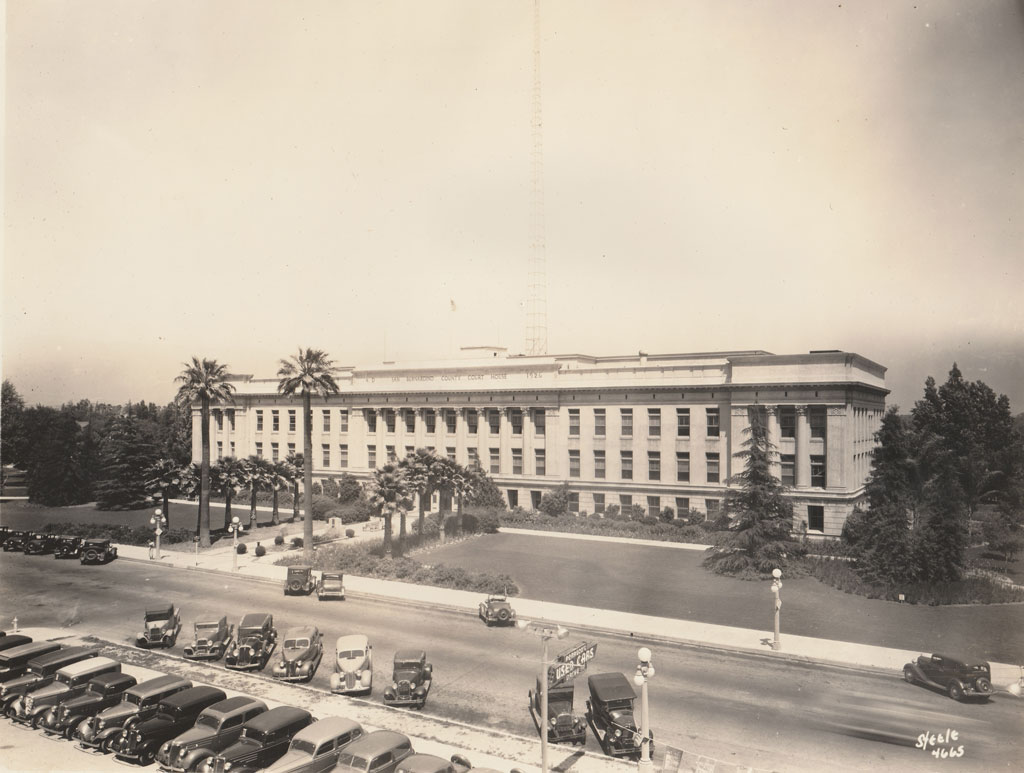
Court House
1875, the first County Court house is built.
The two-story wooden building featured a central clock tower and bell. It was located in the city of San Bernardino on E Street between 3rd and 4th Street.
The building housed the Courts, the Recorder, the Board of Supervisors, and almost every other county office.
The original clock was remounted near the original location of the first Court House on E Street.

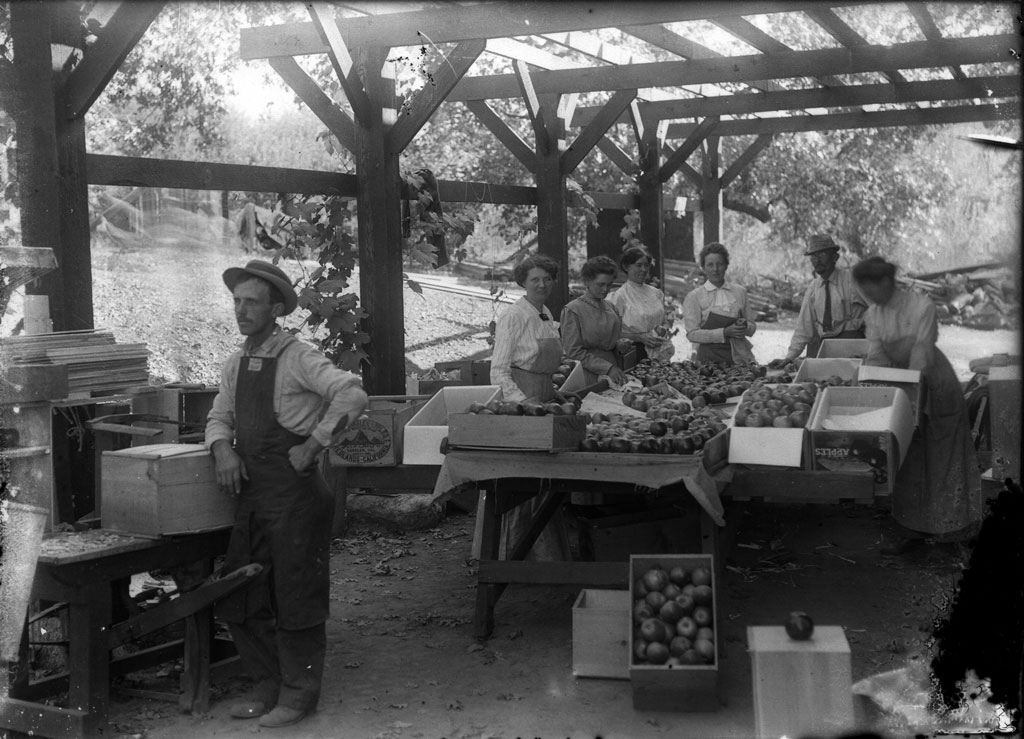
Oak Glen
1876, the first orchard is planted in Oak Glen by Enoch Parrish.
Cahuilla and Serrano had used the area to harvest acorns
Calico
April 6, 1881, prospectors discovered silver in the mountains towards the eastern part of the county, claiming it as the Silver King Mine. The town that soon formed around this claim and others was named Calico and soon was large enough to have its own sheriff and court house.
By the 1900s, the low cost of silver had left the area a ghost town.
1951, Walter Knott, the entrepreneur who created the Knott’s Berry Farm amusement park purchased the Calico townsite.
1966, Knott donated the Calico townsite to San Bernardino County and was made part of the San Bernardino County Regional Parks system.
2005, Calico was proclaimed by Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger to be California’s Silver Rush Ghost Town.

Redlands
1888, Redlands incorporated.
Originally part of the territory of the Morongo and Aguas Calientes tribes of Cahuilla people.
1881, Frank E. Brown and E. G. Judson purchased land and secured water rights.
1885, construction completed on Big Bear Dam which supplied water to city laid out by Judson and Brown.
Court House and Hall of Records
1891, Hall of Records constructed.
Various departments had outgrown the old court house building after the land booms of the 1880s, prompting the need for a new structure. To conceal the size of the project, it was referred to as an “extension” of the courthouse; however, the new structure dwarfed the old one. The Clock was removed from the older structure to place at the front of the extension.
1923, an earthquake struck the area and the courthouse was severely damaged.


Ontario
1891, Ontario incorporated.
1881, brothers George and William Chaffey, purchased land with water rights from San Antonio Creek, calling their venture the Ontario Model Colony, named after their home province of Ontario, Canada.
The Ontario Model Colony master plan called for methods of distributing water over the region to each farm lot in cement pipes. Each holder was to share in the water proportionately to his holding irrespective of distance from the source.
Riverside
1892, Riverside County formed from parts of San Bernardino County.
1891, Hall of Records constructed.
Various departments had outgrown the old court house building after the land booms of the 1880s, prompting the need for a new structure. To conceal the size of the project, it was referred to as an “extension” of the courthouse; however, the new structure dwarfed the old one.
The citizens of Riverside protested the new Hall of Records structure as a misuse of county funds and submitted a proposal to the State legislature to create Riverside County. The proposal was accepted.
San Bernardino County 1900-1950
Upland
1906, Upland incorporated.
Ontario submitted to annex into the city the land where the Upland post office and the Santa Fe railroad station were located.
A petition seeking incorporation was successfully voted upon.
Chino
1910, Chino incorporated.
The Tongva had a settlement called Wapijangna in the Santa Ana River watershed.
1841, Isaac Williams is granted the Rancho Santa Ana del Chino.
1887, Richard Gird purchased parts of the Rancho Santa Ana del Chino and created a map and subdivided the land.
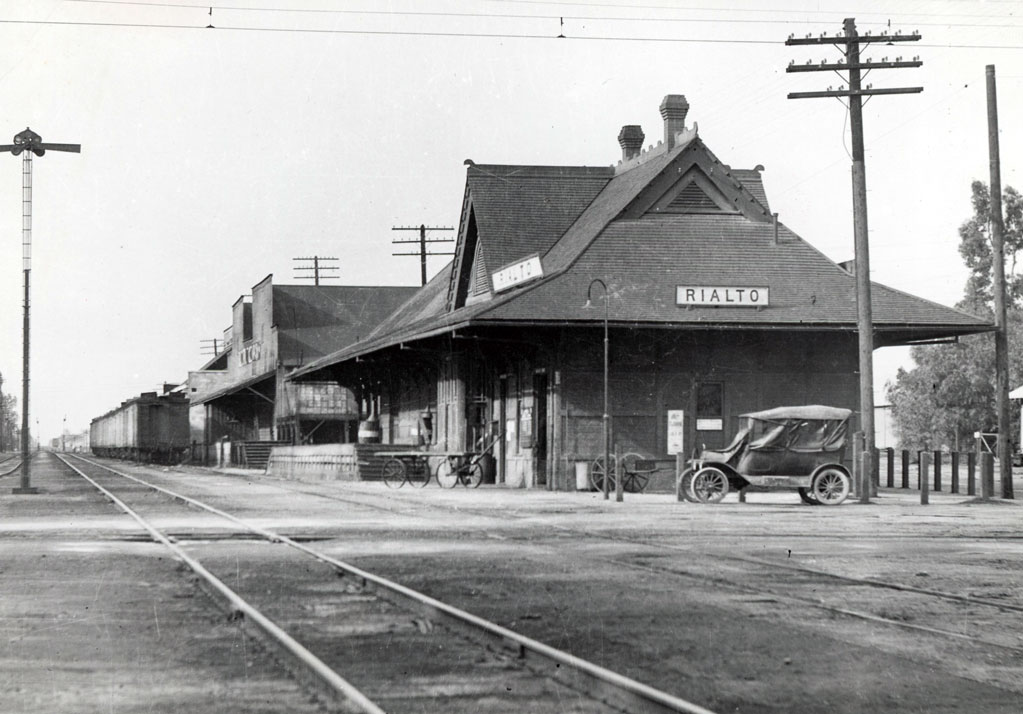
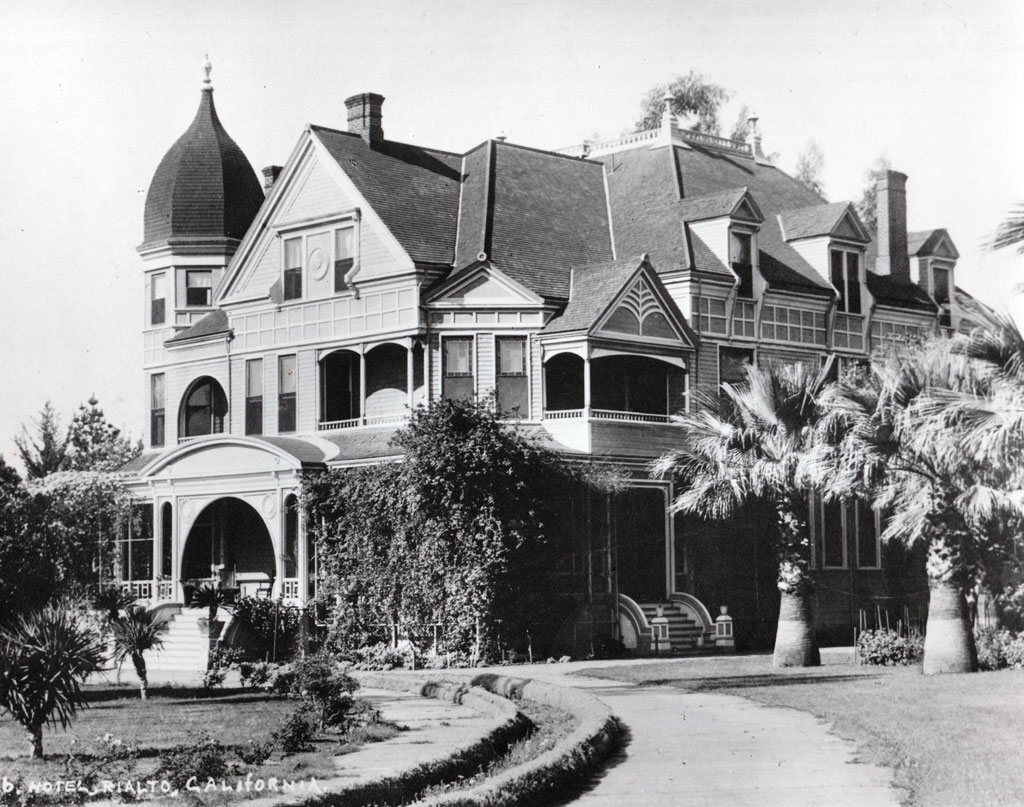
Rialto
1911, Rialto incorporated.
The Serrano had lived in the area since 1500.
1887, a townsite was laid out by the Semi-Tropic Land and Water Company. The company also laid out the town sites of Bloomington, San Sevaine, and what is now Fontana.
Needles
1913, Needles incorporated.
1859, the United States Army established Camp Colorado (later changed to Ft. Mojave) on the east side of the Colorado River
1883, the first railroad crossed the Colorado River from Topock in Arizona Territory to the present site of Needles, named after a distinctive group of rock pinnacles, mountain peaks in Mohave County, Arizona.
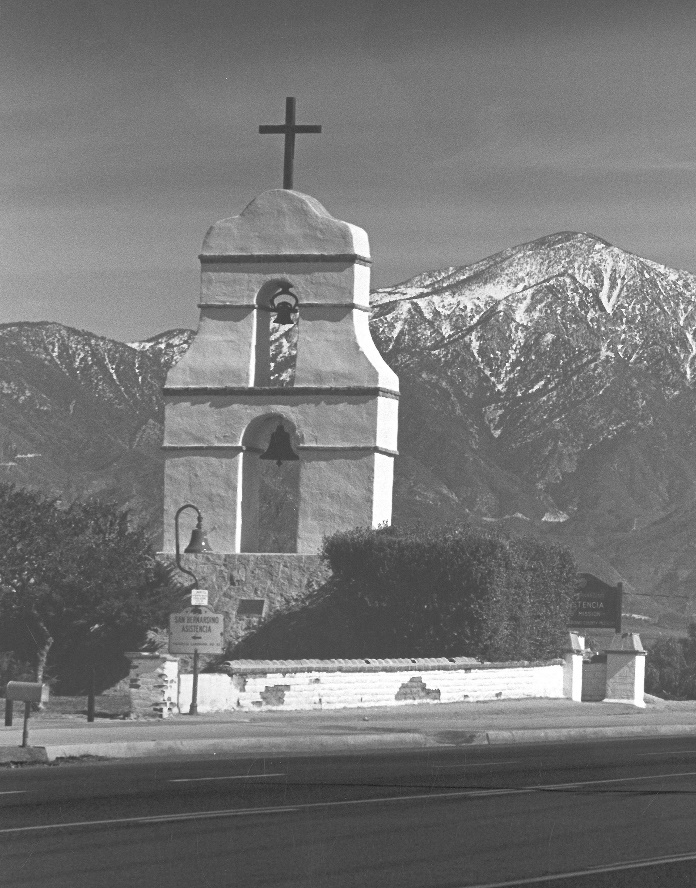

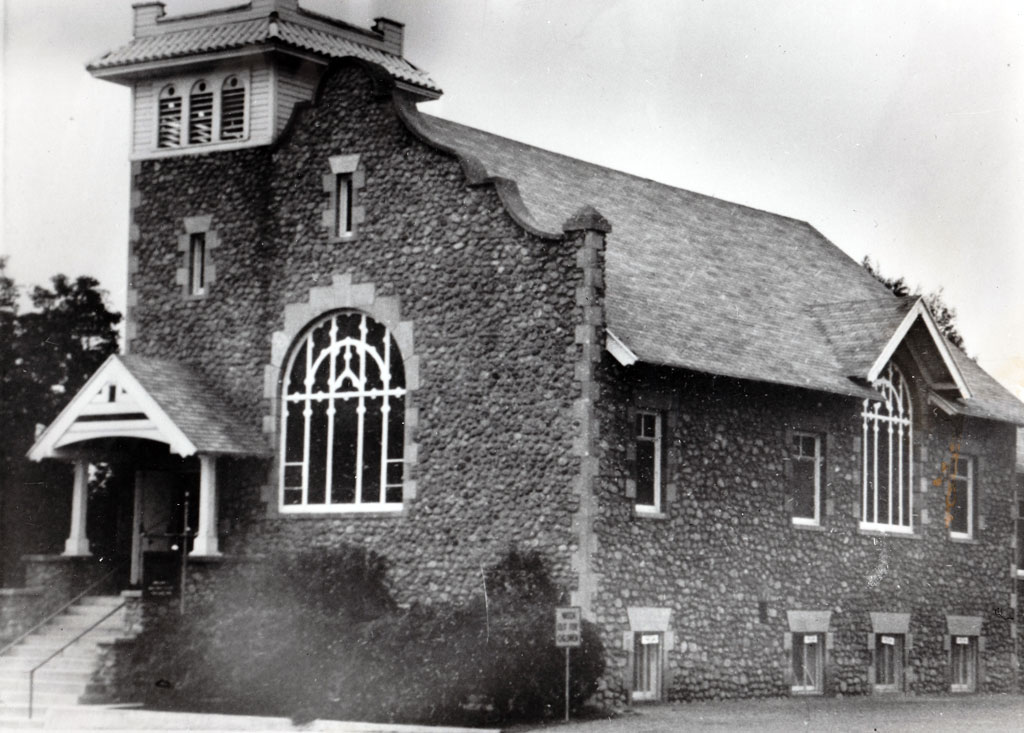
Asistencia
1925, San Bernardino County acquired the Asistencia/Estancia property.
1819, the Mission San Gabriel started an outpost approximately one mile east of the present site.
1830, Juan Alvarado, a majordomo for the Mission San Gabriel, relocated the Estancia to its present site and constructed a 14-room complex.
1842, the Rancho San Bernardino granted to José del Carmen Lugo, José Maria Lugo, Vincente Lugo, and Jose Diego Sepulveda, included the Estancia.
1851, Lugo’s sold the Rancho to members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
1859, Dr. Ben Barton purchased 640 acres including the Estancia.
1937, the Works Progress Administration complete the reconstruction of the structure adding a bell tower.
Court House
1926, Court House constructed.
1923, an earthquake struck the area and the old courthouse were severely damaged.
County Supervisors requested architect Howard E. Jones determine whether it was more economical to repair/upgrade the old damaged courthouse, or build an entirely new structure.
1998, courthouse was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.
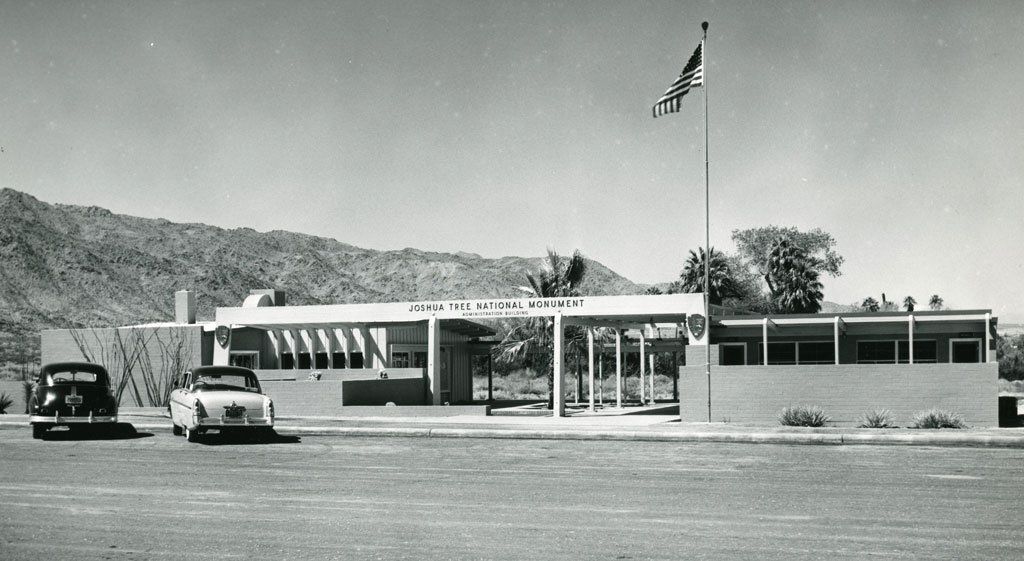


Joshua Tree National Monument
1936, Joshua Tree National Monument is formed with 825,000 acres being set aside as Joshua Tree National Monument.
Minerva Hoyt, a Pasadena resident fond of desert plants, became concerned about the removal of cacti and other plants as a result of land development and cactus poachers and led the campaign.
The earliest known residents of the land were the people of the Pinto Culture, who lived and hunted here between 8000 and 4000 BCE. Later residents included the Serrano, the Cahuilla, and the Chemehuevi peoples.
October 31, 1994, as part of the Desert Protection Bill passed into law by Congress, Joshua Tree National Monument was elevated to park status.
Fort Irwin
August 8, 1940, President Franklin D. Roosevelt set aside approximately 1,000 square miles in the Mojave Desert 38 miles north of Barstow as an anti-aircraft training range.
December 1942, with active desert training for over 60,000 troops it was re-designated as Camp Irwin.
Named in honor of Major General George LeRoy Irwin, a WWI field commander who led his 57th Field Artillery Brigade during the Marne-Argonne offensives against the Germans. General Irwin was one of the first recipients of the Congressional Medal of Honor for distinguished gallantry, decorated with the Legion of Honor, the Croix de Guerre of France, and the Distinguished Service Medal of the United States.
1946, Camp Irwin was deactivated and turned over to the War Administration and renamed a sub-installation of Fort Mac Arthur in Los Angeles.
1961, the post was renamed once more as Fort Irwin and additionally classified as a permanent installation.
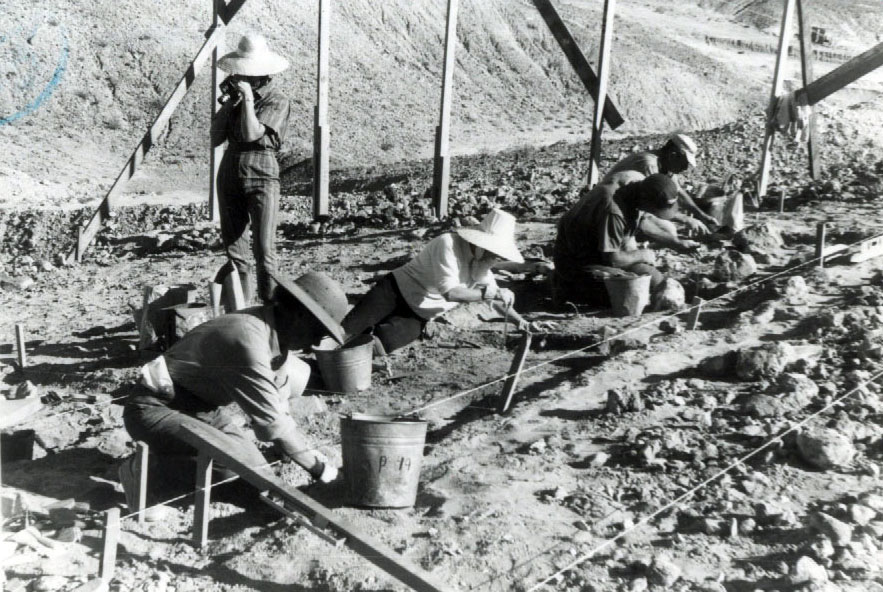
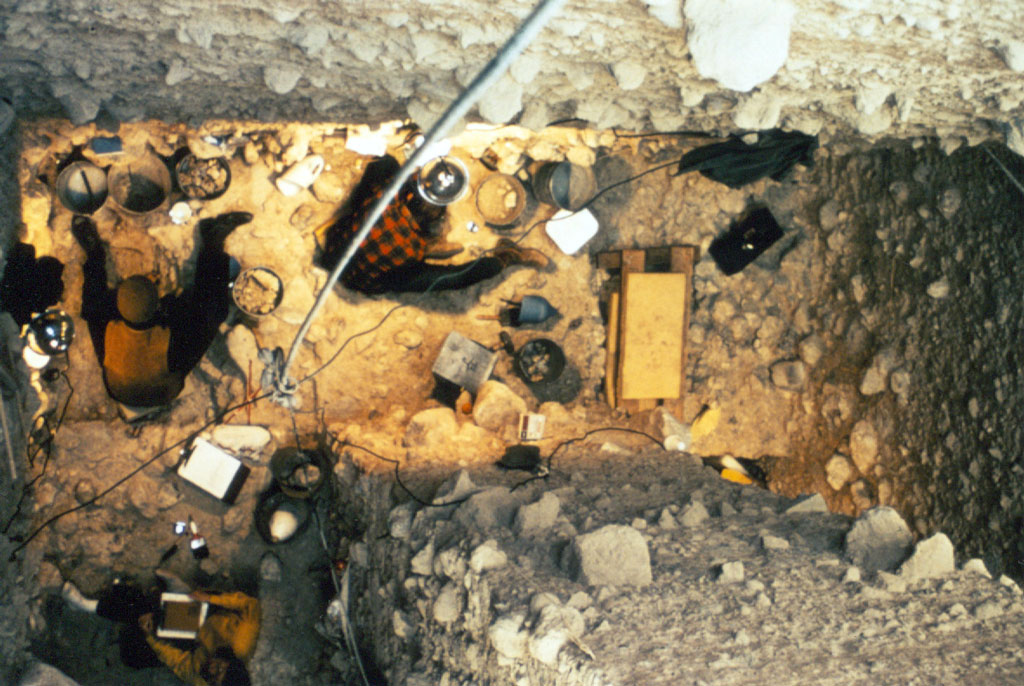
Calico Early Man Site
1942, amateur geologist found artifacts resembling primitive stone tools east of Barstow embedded in the sediments of the shoreline of an ancient Pleistocene era lake, that dried up 18,000 years ago.
1954, San Bernardino County archaeologist Ruth Simpson took artifacts to renowned scientist Louis Leakey, discoverer of early man sites in Africa.
1963, Leakey studied the site and concluded that the pieces of rock found at Calico “unquestionably” were human-made artifacts. The area became known as the Calico Early Man Site.
No discoveries of human remains have been made at the site, which fuels opposing views as to whether the artifacts found are man-made or caused by natural forces. The site is under the control of California’s Bureau of Land Management.
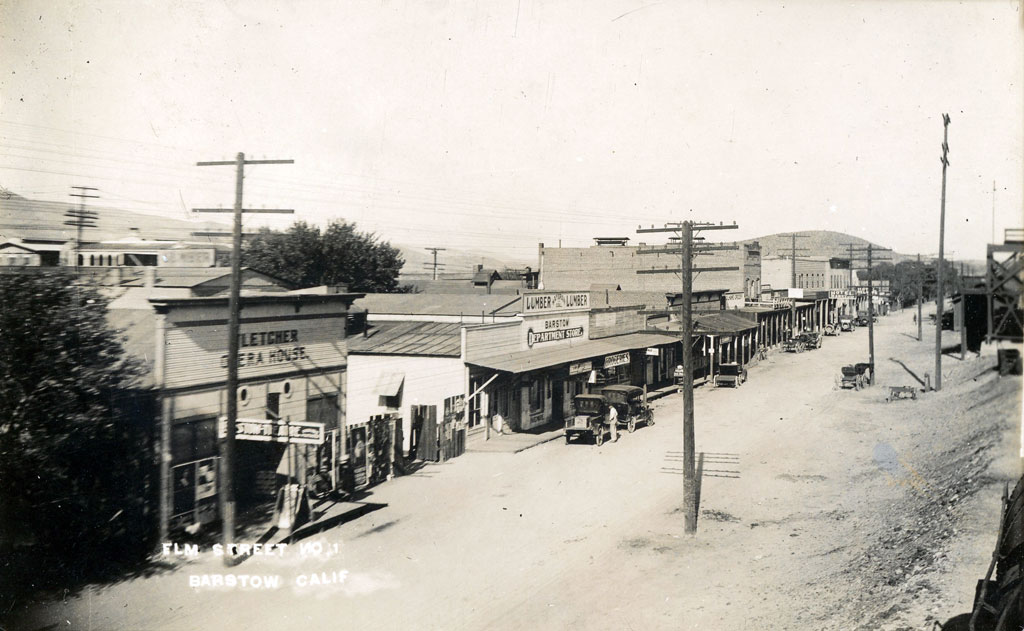
Barstow
1947, Barstow incorporated.
Paiute, Mojave, and Chemehuevi tribes used the oasis for 100s of years.
1850s, the area was known as Grapevine for the local grapes that grew in the oasis.
1880s, was named Waterman Junction after Robert W. Waterman who had filed two of the biggest silver mine claims in the area.
1884, the new Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railroad named their depot after their president William Barstow Strong, using his middle name.
1886, the town requested their post office be known as Barstow.
San Bernardino County 1950-2000
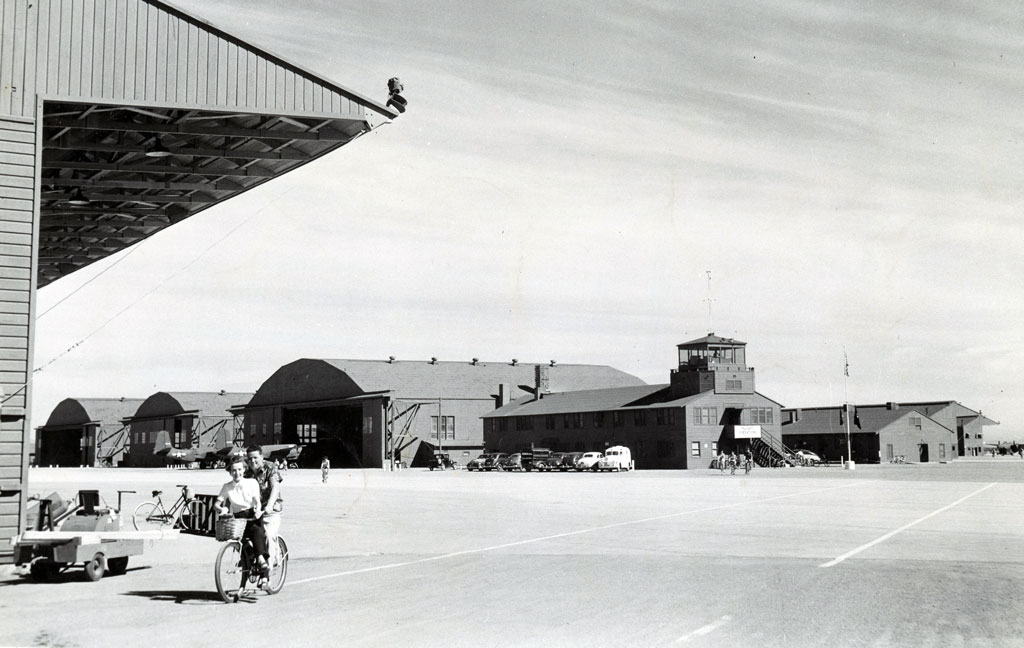

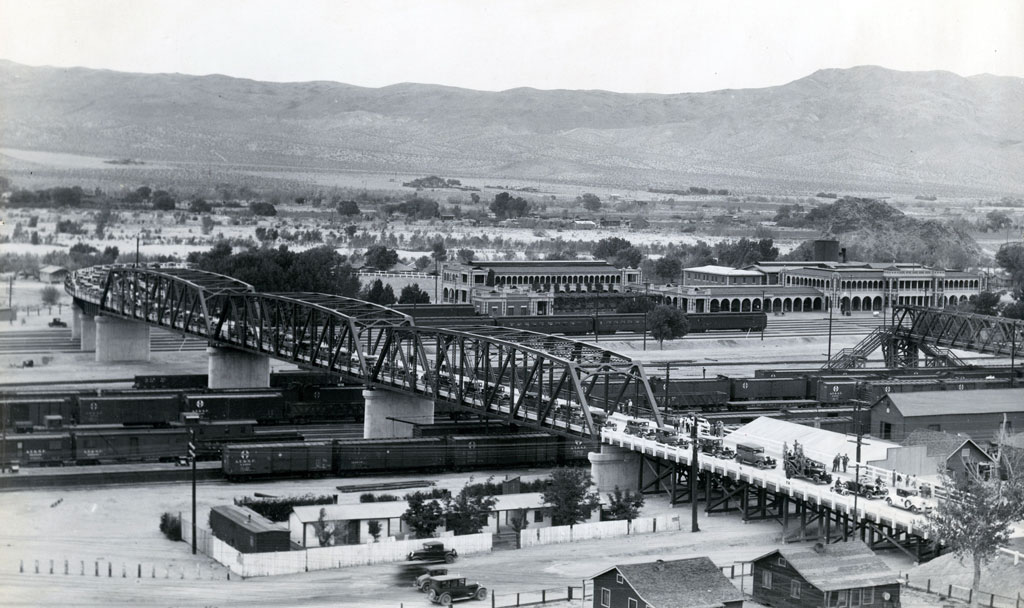
Norton Airbase
1950, a logistics depot and heavy-lift transport facility for the U.S. Air Force in San Bernardino, CA was named for Leland Norton, a San Bernardino native.
Captain Norton flew 15 missions over occupied France during World War II. 1944, on his 16th mission, Captain Norton’s plane took a direct hit from a German anti-aircraft gun. Although severely wounded, he managed to maintain control of the disintegrating aircraft long enough for two of his crew to bail out before perishing in the aircraft. Norton was posthumously awarded the Distinguished Flying Cross and is interred at Mountain View Cemetery.
1988, the base was selected for closure by the Base Realignment and Closure Commission and closed on March 31, 1994.
2011, San Bernardino International Airport need details on when it formed?
George Airbase
1950, the U.S. Army Air Corps Base and Advanced Flying School near Victorville, CA was named after Brigadier General Harold Huston George.
Brigadier General George began his service as a World War I fighter pilot, serving with the 185th and 139th Aero Squadrons. George scored five victories over German planes in the air to qualify as an ace and received the Distinguished Service Cross for heroism in action.
1941, during World War II, he was promoted to brigadier general. April 29th, 1942, George was killed in a ground accident at Batchelor Field, southeast of Darwin, Australia.
1992, George Air Force Base was officially decommissioned by Congress under the Base Realignment and Closure program.
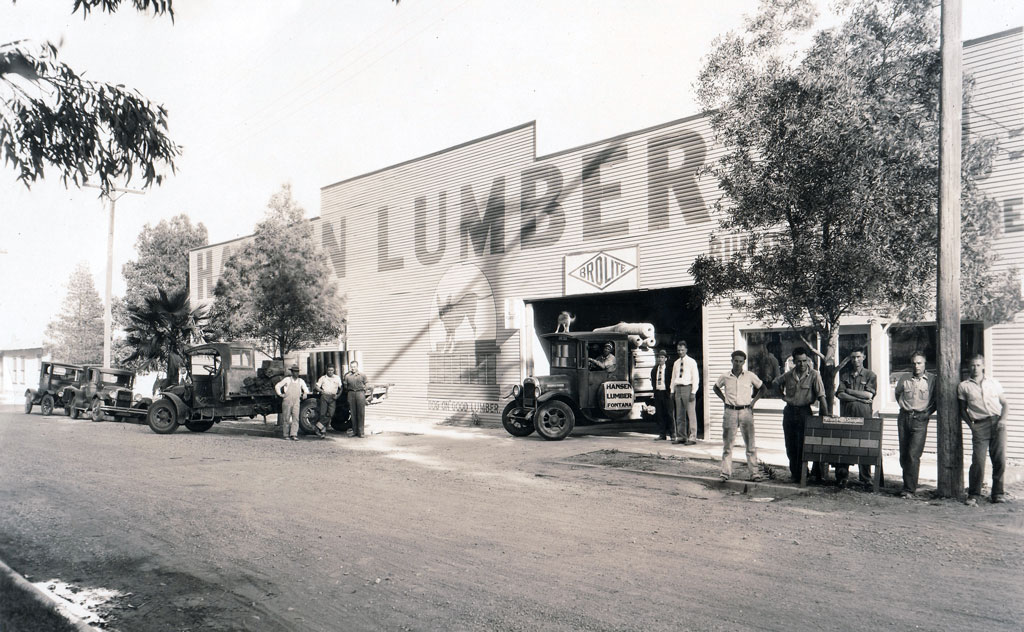
Fontana
1952, Fontana incorporated.
1890, Southern California Railway started a station called Rosena.
1905-1906, Azariel Blanchard Miller purchased 17,000 acres in Rosena calling his venture the Fontana Water and Land Company.
1913, Mr. Millers’ mother Eliza christened the town Fontana, by striking the flagpole on the base with a bottle of local grape juice.
29 Palms Marine Base
1952, Camp Pendleton Base Headquarters designated 930 square miles of desert as the Camp Detachment, Marine Corps Training Center.
1957, the base was designated as the Marine Corps Base, Twentynine Palms.
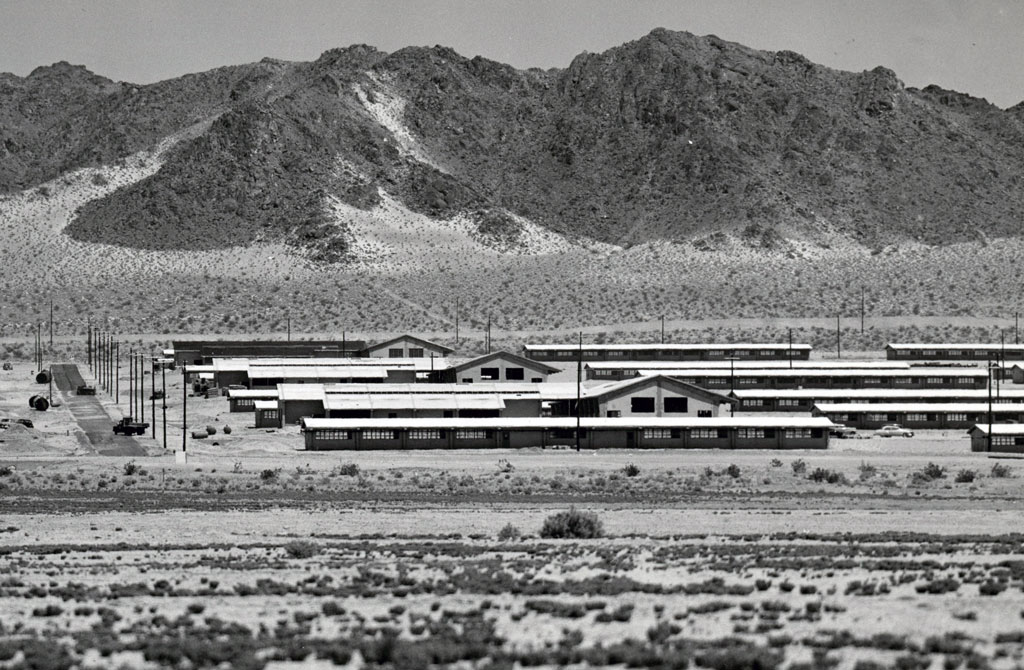
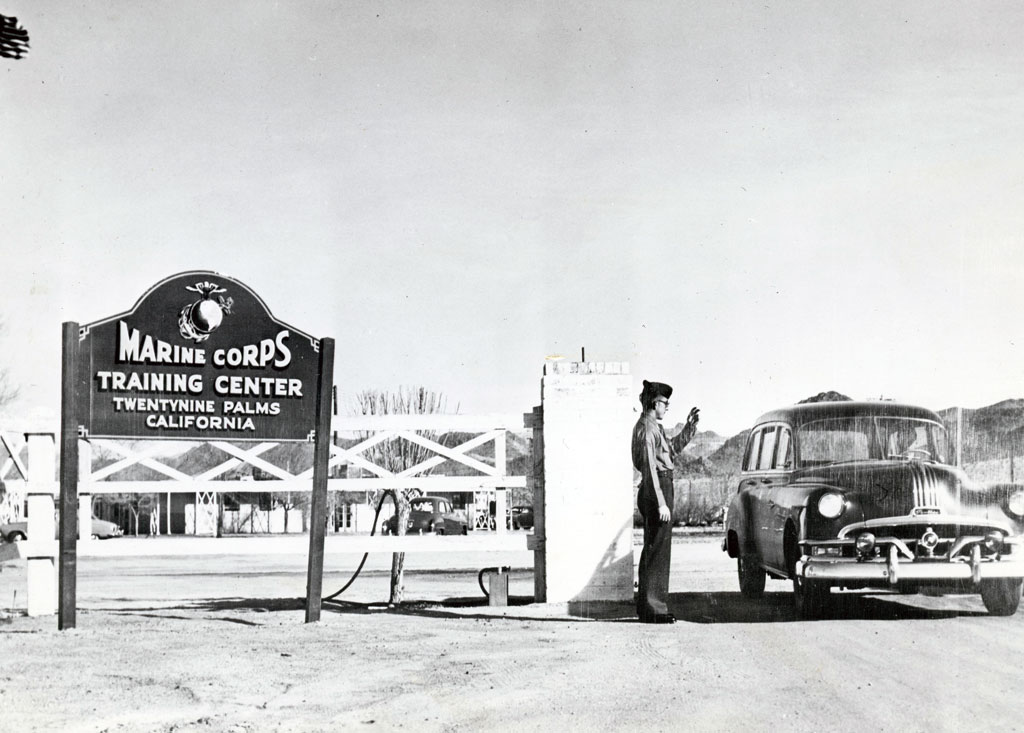


29 Palms Marine Base
1954, Yucaipa Adobe sold to San Bernardino County Museum.
1840s, Diego Sepúlveda one of the recipients of the Rancho San Bernardino built an Adobe.
1851, Rancho Sand Bernardino sold to members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
1852, James Waters purchased the abode and improved and expanded the with some of the original Sepulveda Adobe used in the construction.
1869, Waters sold to John Dunlap roughly 3,000 acres, or half of present-day Yucaipa, including the adobe.
1903, the Dunlap Brothers formed and incorporated The Yucaipa Water and Land Company.
The Dunlap’s sold the Adobe in 1954 to San Bernardino County and is considered the oldest structure in the county and sections predate California as a state.
Montclair
1956, Monte Vista incorporated, changing name to Montclair in 1958.
1897, Mrs. Edward Fraser founded The Township of Marquette.
1900, a 1,000-acre tract of land within the township was surveyed and named Monte Vista.
Fearing annexation by a neighboring city, long-time residents formed the Monte Vista Improvement Association.
The Association proposed city incorporation of the Monte Vista Land Tract and the residents were asked to vote on a city incorporation proposal.

Victorville
1962, Victorville incorporated.
Since ancient times, indigenous peoples have used the many networks of trails in the East Mojave Desert for migration and trade. The Serrano-Vanyume village of Tobiabit were located here.
1880s, a railroad station and telegraph office was named Victor, after the California Southern Railroad’s construction superintendent Jacob Nash Victor.
1901, at the suggestion of local postmaster Abbey Turner, the U.S. Post Office Department changed the town name to Victorville due to postal confusion with the town of Victor, Colorado.
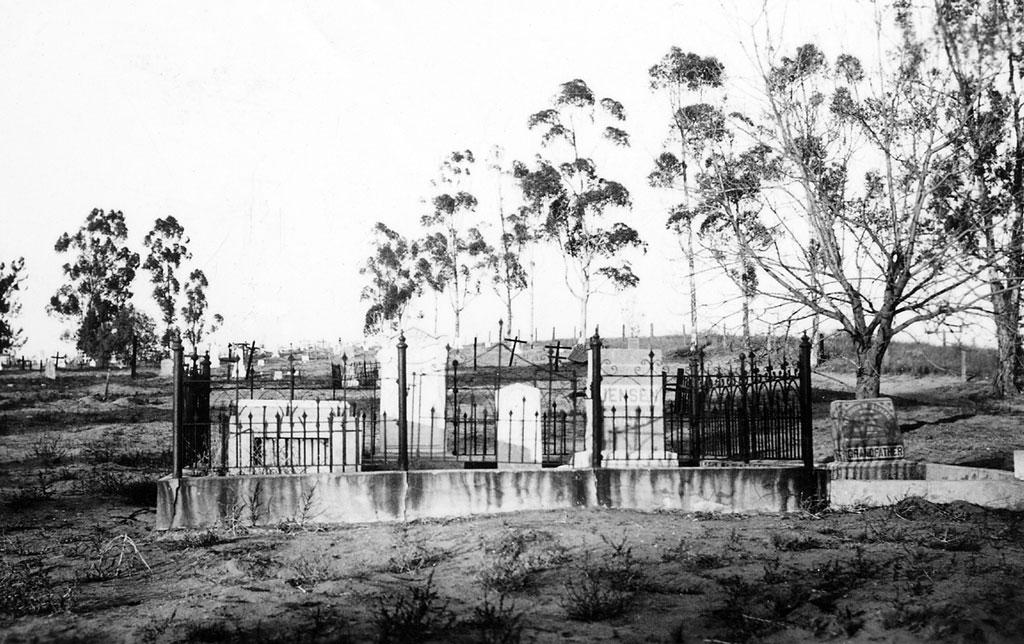
Aqua Mansa
1966, Agua Mansa Pioneer Cemetery was accepted by the county and became part of the County Museum.
1955, a descendant of the original Agua Mansa families established “Friends for the Preservation of the Agua Mansa Pioneer Cemetery” and the volunteers of this group refurbished the cemetery, fenced it off and added a gate.
Loma Linda
1970, Loma Linda incorporated.
1886, investors purchased 260 acres south of the city of San Bernardino establishing the Mound City Land and Water Company.
In the late 1890s, Mound City was purchased by a group of Los Angeles physicians and businessmen who in 1900 changed their name to the Loma Linda Association.
In 1904, the property came to the attention of the Seventh-Day Adventists, through the efforts of prominent author, Ellen G. White. The Seventh-Day Adventist Church purchased the property and established a sanitarium and a nursing school.
1906, Nursing instruction commenced and in 1910 the Loma Linda Medical College opened.
Adelanto
1970, Adelanto incorporated.
1915, Earl H. Richardson sold his patent for an electric iron and purchased land for $75,000 located about 9 miles northwest of current Victorville in the Victor Valley area of the Mojave Desert.
Richardson developed one of the first planned communities in Southern California, by subdividing his land into one-acre plots. He hoped to sell to veterans with respiratory ailments suffered during World War I.
His planning laid the foundation for what would be the City of Adelanto.
In early 1941, during World War II, the Victorville Army Air Field was established within Adelanto, later known as George Air Force Base.
Rancho Cucamonga
1977, Rancho Cucamonga incorporated.
In 1839, Tiburcio Tapia was granted the Rancho Cucamonga. The land grant encompassed 13,000 acres.
Tapia gave the Rancho to his daughter Maria Merced Tapia and her husband Leon Victor Prudhomme.
In 1859, John Rains purchased the Rancho from Prudhomme and set out additional grapevines and constructed a brick house on the property at a cost of about $18,000.
The City of Rancho Cucamonga incorporated in 1977 to include the original rancho, as well as parts of the historic communities of Grapeland, Etiwanda, and Alta Loma.
Grand Terrace
1978, Grand Terrace incorporated.
1877, the Colton Land and Water Company, which later became the Colton-Terrace Water Company, organized bringing water from the artesian wells. 1898, the name Grand was added to Terrace to refer to the area when the Riverside Highland Water Company started developing the area.
1904, Charles Patton and M. L. Howell purchased 300 acres and organized land in sections of 8 to 20 acres, naming their tract Grand Terrace.

Twentynine Palms
1987, Twentynine Palms incorporated.
1855, The first recorded exploration of Twentynine Palms was made by desert surveyor Colonel Henry Washington encountered American Indians, principally from the Chemeheuvi tribe, living in the region and near a spring they called “Mar-rah,” meaning “land of little water.”
The early Native American inhabitants (Serrano, Chemheuvi, and Cahuilla) were followed in the 1870’s by prospectors in search of gold.
After World War I, many veterans returned to their homes suffering from tuberculosis and the effects of mustard gas that had been used in combat.
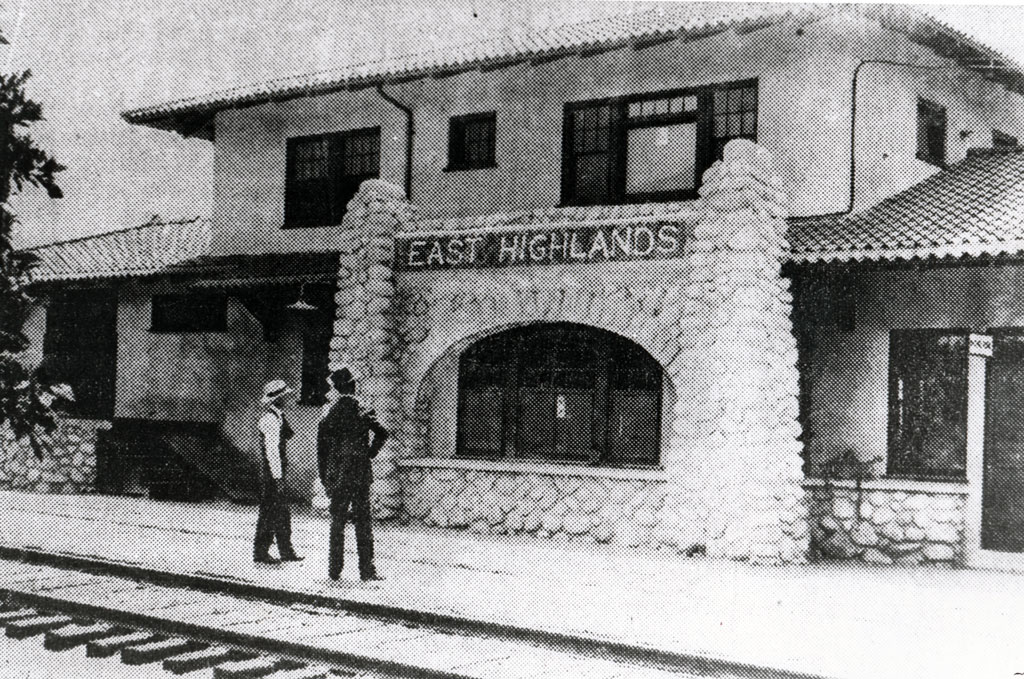
Highland
1987, Highland incorporated.
1858, Lewis Cram and Frederick Van Leuven constructed the Cram-Van Leuven ditch, extending from the Santa Ana River entrance to their land in East Highlands.
Hesperia
1988, Hesperia incorporated.
1887, the California Southern Railroad, later to become the Santa Fe, completed laying tracks and started a town site with a small depot only 15 feet wide and 20 feet long.
The Railroad named the town after Hesperus, the Greek god of the west.
1954, land developer M. Penn Phillips and his silent financial partner, the famous boxer Jack Dempsey, financed the building of roads and land subdivisions.
They purchased 23,000 acres and divided the land into 30,000 parcels.
Chino Hills
1991, Chino Hills incorporated.
1979, the Chino Hills specific plan is initiated by the County calling for the development of 18,000 acres.